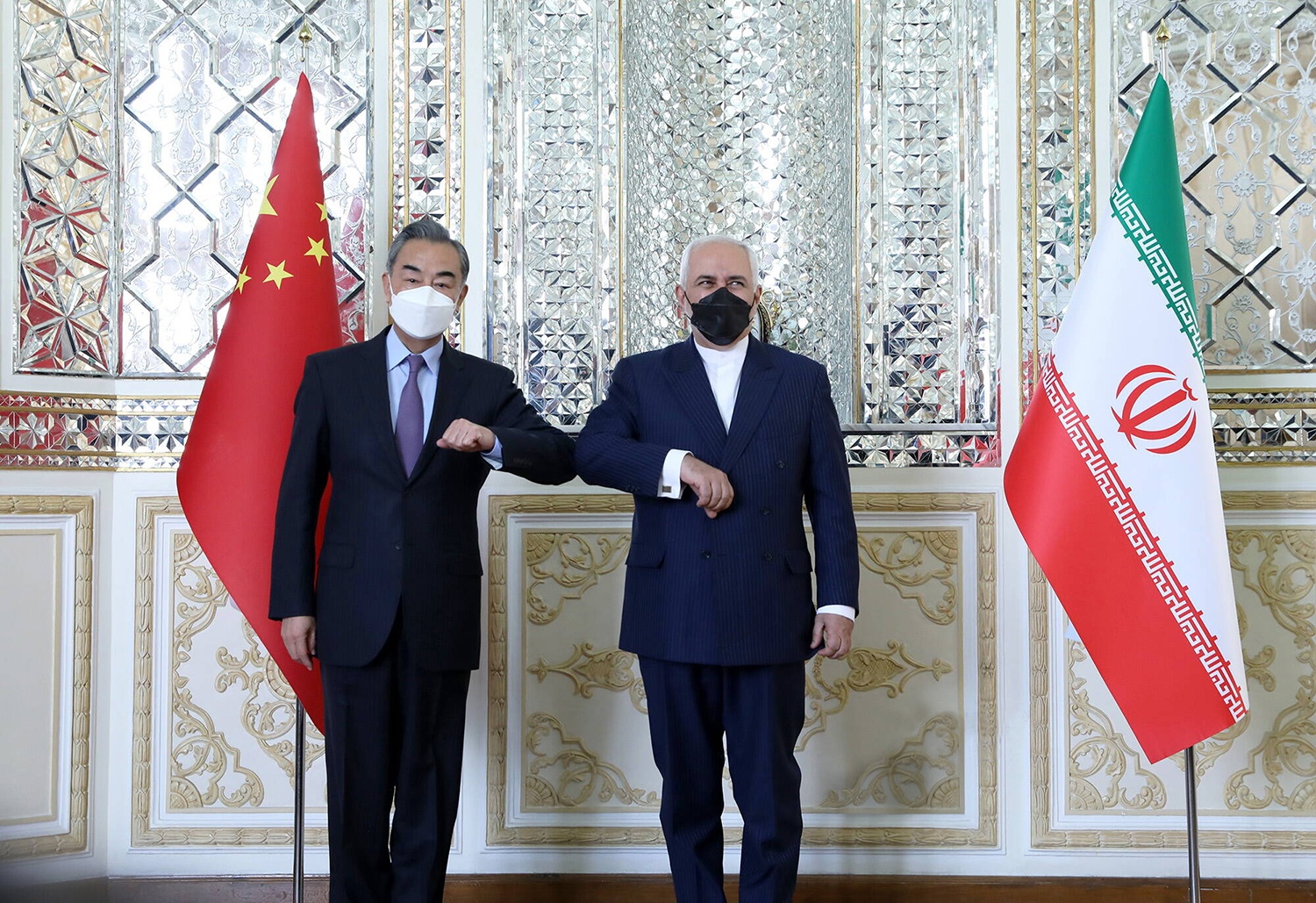
Iran and China have strengthened their ties. The regional and international geopolitical impact of the Strategic Partnership Cooperation will move Iran into China’s orbit and end Iran’s global isolation.
Scarlett Yan, 18 April 2021
A historic 25-year deal between China and Iran covering a wide range of issues has the potential to reshape the geopolitical landscape. Ultimately, this agreement might shift the balance of power in the Persian Gulf region. This agreement has solicited a differentiated response in the global media also owing to its regional and global geopolitical impact.
What’s The Deal
On March 27, Chinese Foreign Minister Wang Yi and his Iranian counterpart Mohammad Javad Zarif reached a 25-year cooperation agreement in Tehran. The signing of this deal was a follow-up to the new partnership between China and Iran. Since 2016, China and Iran have established a comprehensive strategic partnership, and both sides had agreed to conclude a comprehensive cooperation plan. Within China’s diplomatic strategy, this partnership with Iran represents a higher level of diplomatic relationship, second only to the partnership between China and Russia.
The agreement was preceded by 5 years of intense negotiations. The draft agreement was passed by the Iranian government in June 2020. As the year 2021 marks the 50th anniversary of China-Iran diplomatic relations, the agreement is considered a tribute to this anniversary.
The main content of the deal can be titled “oil for investment,” a practice China has also employed in some African countries. According to the draft agreement, China will invest a total of $400 billion in Iran in the next 25 years, covering dozens of areas and nearly 100 projects, including, i.a., banking, telecommunications, medical care, infrastructure and information technology. In exchange for these investments, Iran will supply China with oil at a discount during this period. Moreover, both sides have agreed to strengthen military cooperation.
There are several important facts about this deal worth mentioning. The most important one is the settlement of payments. According to the agreement, oil payments and trade between China and Iran would be settled in Chinese Renminbi and the newly launched digital Renminbi, abandoning the international settlement currency–the US dollar. This clause will pave the way for China to challenge the global financial dominance of the US dollar.
At present, the agreement still awaits approval by Iran’s parliament, and it remains to be seen whether it will pass or not. China’s South China Morning Post described the imbalance between the two partners, noting that while Tehran hopes to benefit from cooperation, both sides are aware this is not an agreement among equals, as Iran needs China much more than China needs Iran.
What Are The Implications Of The Deal
From China’s point of view, the signing of the deal was business as usual. Internationally, the agreement has raised some concerns, especially among the western media, which regarded the signing of the comprehensive cooperation plan between China and Iran as an act of “China’s continuous expansion of its influence in the Middle East.” This interpretation by the West reflects the geopolitical competition among the major powers in the Middle East.
At a press conference on March 29, Zhao Lijian, spokesperson of the Chinese Foreign Ministry, reiterated that the signing of the China-Iran comprehensive cooperation plan “is not directed at any third party.” On the same day, China’s Ambassador to Iran, Chang Hua, also published an article through the Iranian National News Agency, emphasizing that the “China-Iran cooperation is based on mutual respect, mutual benefit and win-win results. We will neither engage in a ‘zero-sum game’ nor target at a third party.” However, the deal remains a sensitive topic in the current volatile situation in the Middle East by deepening and strengthening China and Iran’s cooperation in many areas, including diplomatic, economic and military ties.
The deepening of ties between China and Iran will have major regional and global geopolitical implications, such as redefining Iran’s position in the Middle East and its relation with the longstanding US allies Israel and Saudi Arabia. It will also partly relieve Iran from the suffering caused by the ongoing US economic sanctions and “maximum pressure” policy, which, ironically, might also have been partly responsible for China and Iran moving closer.
The China, US, and Iran Triangle
Some commentators have pointed out that compared with the inconsistency in US-Iran relations, China is seen by Tehran as a reliable and stable cooperation partner. China also expressed its willingness to act as a peace broker for the Persian Gulf region.
Despite global objections, President Trump’s withdrawal from the JCPOA in May 2018 and the reimposition of sanctions on Iran have not only left the future of the Iran Nuclear deal uncertain but has also led to a more antagonistic relationship between the US and Iran.
Internally the US political pendulum has swung in the other direction after the Biden administration came to power, and there are signs that the US is serious about rejoining the JCPOA. The ongoing Iran negotiations in Vienna are a positive sign that both sides are interested in salvaging the Iran Nuclear Deal. However, the outcome is still uncertain, and so is the timeframe. As one Chinese scholar put it, “After the new U.S. government came to power, on the one hand, both the U.S. and Iran expressed their hope to restart the Iran nuclear agreement, but, in fact, the current contradictory ‘deadlock’ in U.S.-Iran relations has not [yet] been loosened.”
The Iran-China Strategic Partnership Cooperation Agreement could end Iran’s global isolation and strengthen China’s position in the Persian Gulf region.